In recent years, VR training in healthcare has emerged as a transformative tool, offering innovative solutions that enhance both education and patient care. As healthcare systems worldwide face increasing pressures to deliver high-quality service, the integration of virtual reality technology provides an immersive and interactive learning environment. Dr. Emily Thompson, a leading expert in medical education, aptly stated, "VR training in healthcare not only bridges the gap between theory and practice but also empowers healthcare professionals to develop skills in a safe, controlled environment."
The capacity for simulation in VR allows trainees to experience real-life scenarios without the risks associated with traditional training methods. This not only boosts their confidence but also ensures they are better prepared for complex situations they may encounter in actual practice. Furthermore, VR training fosters collaboration among healthcare professionals, enhancing team-based approaches crucial for patient care.
As we delve deeper into how VR training in healthcare is revolutionizing educational practices and patient interactions, it becomes evident that this technology is not merely a trend but a foundational shift towards more effective healthcare delivery. The following sections will explore the key benefits, potential hurdles, and future prospects of incorporating VR into healthcare education and patient care.

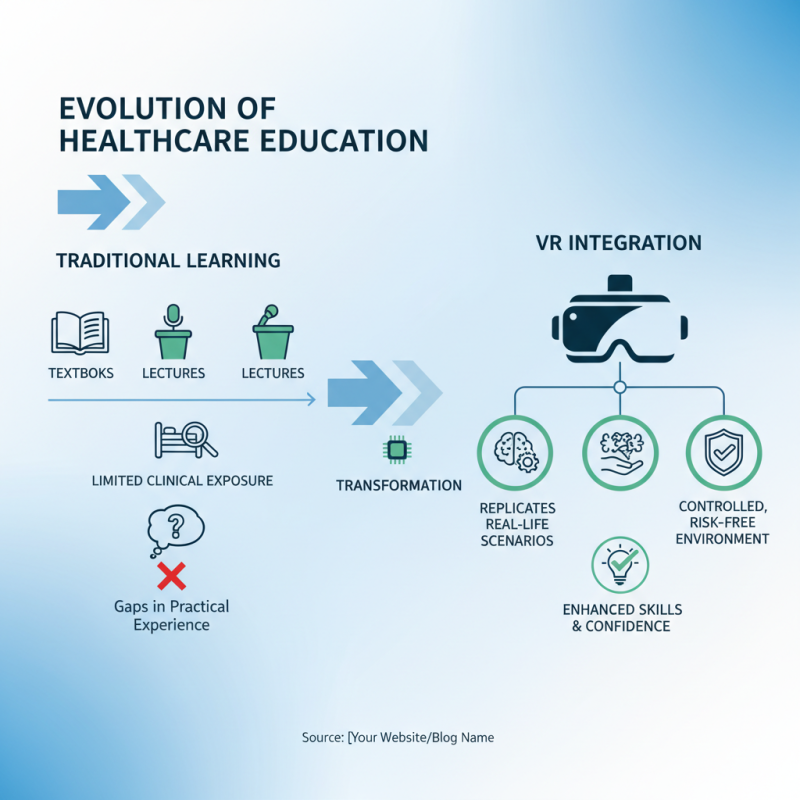
The evolution of healthcare education has witnessed a significant transformation with the integration of Virtual Reality (VR) technology. Traditionally, medical training has relied heavily on textbooks, lectures, and limited clinical exposure, which could lead to gaps in practical experience. VR technology introduces immersive simulations that replicate real-life medical scenarios, allowing students and professionals to refine their skills in a controlled environment. This not only enhances the learning experience but also instills confidence, as practitioners can rehearse procedures multiple times without the fear of harming real patients.
Moreover, VR training fosters a deeper understanding of complex medical concepts by providing visual and interactive elements. For instance, anatomy can be explored in three dimensions, enabling learners to visualize spatial relationships between organs and systems more effectively. This interactive aspect of VR education is invaluable for retaining knowledge and understanding the intricacies of human physiology. By bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, VR technology is positioning itself as a cornerstone for evolving healthcare training and improving overall patient care outcomes.
Virtual Reality (VR) training is increasingly redefining the landscape of medical education, offering unprecedented advantages for healthcare professionals. One of the primary benefits is the immersive learning environment that VR provides. This technology enables practitioners to simulate complex medical procedures and scenarios in a risk-free setting, allowing them to hone their skills without the immediate pressure or consequences of real-life situations. By engaging in realistic simulations, healthcare professionals can enhance their decision-making abilities, improve their technical skills, and gain confidence in their clinical competencies.
Moreover, VR training fosters enhanced collaboration among medical teams. Through virtual environments, professionals can engage in team-based training exercises that mimic real-world medical emergencies. This collaborative approach not only strengthens communication and teamwork skills but also prepares healthcare workers to function effectively in high-stress situations. Furthermore, VR training can be customized to address specific learning needs and complexities, allowing for a more personalized educational experience that promotes retention and application of knowledge in actual patient care scenarios. As a result, the integration of VR training into medical education is setting new standards for how professionals are prepared to deliver quality care in today’s dynamic healthcare landscape.
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Healthcare |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Learning Retention | VR simulations engage learners actively, improving information retention. | Better prepared professionals lead to improved patient outcomes. |
| Realistic Scenarios | Allows students to practice in a risk-free environment, simulating real-life scenarios. | Increases confidence in dealing with emergency situations. |
| Immediate Feedback | Instructors can provide instant evaluations during VR training. | Facilitates quick learning and correction of mistakes. |
| Accessibility | VR training can be accessed remotely, allowing for flexible learning. | Expands educational opportunities for rural and underserved regions. |
| Team Training | Facilitates collaborative practice among healthcare teams in VR settings. | Enhances team dynamics leading to better patient care. |
Virtual reality (VR) is increasingly being recognized for its transformative potential in clinical settings, particularly in enhancing patient care. By immersing healthcare professionals in simulated environments, VR enables them to practice complex procedures and scenarios without the risks associated with real-life patients. For instance, practitioners can train for surgeries, emergency responses, and patient interactions, gaining invaluable experience that translates directly into improved confidence and competence during actual medical situations.
Moreover, VR applications are not limited to training practitioners; they extend to patient care as well. Patients can benefit from VR experiences designed to alleviate anxiety before procedures, provide education about their conditions, or even facilitate rehabilitation exercises in an engaging manner. For instance, VR can be utilized in pain management by distracting patients during uncomfortable treatments or physical therapy sessions.
By incorporating VR into the healthcare landscape, providers can offer more empathetic, effective, and tailored care, significantly improving patient outcomes and overall satisfaction.
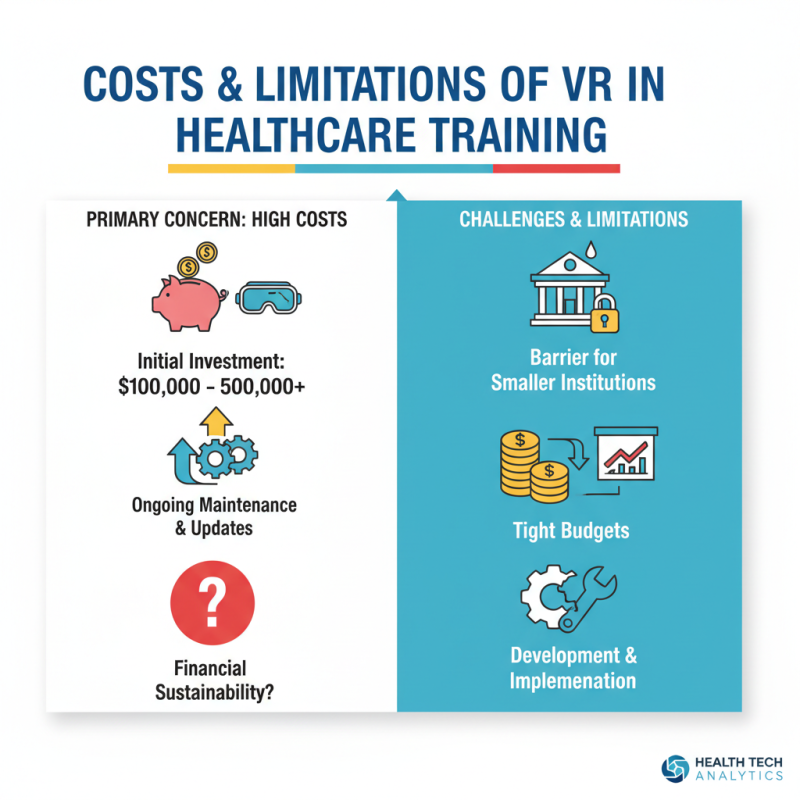
While VR training is heralded as a transformative tool in healthcare education, it is not without its challenges and limitations. One of the primary concerns is the high cost associated with developing and implementing VR training programs. According to a 2022 report by the Global Healthcare VR Market, the initial investment for high-quality VR simulations can range from $100,000 to over $500,000, making it difficult for smaller institutions to adopt this technology. Furthermore, ongoing maintenance and updates to content further escalate costs, raising questions about financial sustainability for healthcare organizations operating on tight budgets.
Another significant limitation of VR training in healthcare involves the need for technological infrastructure and skilled personnel. A survey conducted by the American Medical Association indicated that over 40% of healthcare facilities lack the necessary hardware and software to effectively utilize VR training. Moreover, staff must receive adequate training to operate the technology effectively, which can divert resources from patient care. Concerns about the potential for VR experiences to create unrealistic expectations or oversimplify complex patient interactions also persist, emphasizing the necessity for balanced integration of VR training within broader educational frameworks in the healthcare sector.
The integration of Virtual Reality (VR) in healthcare is set to transform the landscape of medical education and patient care. As various hospitals and educational institutions adopt immersive technologies, VR is becoming a pivotal tool for training healthcare professionals. By simulating real-life medical scenarios, trainees can engage in hands-on practice without the risk associated with working on actual patients. This experiential learning approach enhances their skills significantly, fostering a deeper understanding of complex procedures and patient interactions.
Looking ahead, the role of VR in shaping healthcare delivery is profound. It not only facilitates advanced training for practitioners but also enhances patient engagement and treatment outcomes. For instance, VR can be utilized for patient education, allowing individuals to visualize their medical conditions and treatment plans interactively. Furthermore, by offering virtual environments for therapeutic purposes, such as pain management and rehabilitation, VR can contribute to improved patient experiences and satisfaction. As this technology continues to evolve, it promises a future where healthcare becomes more efficient, personalized, and accessible.






