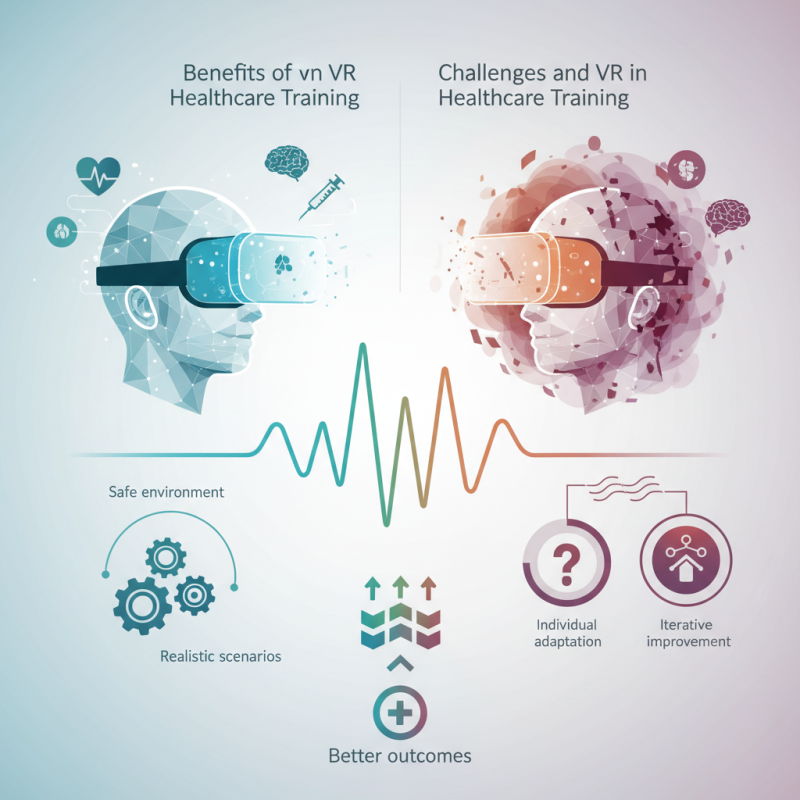
Virtual Reality (VR) has transformed various fields, and healthcare is no exception. VR Healthcare Training offers immersive experiences that enhance learning outcomes. It allows medical professionals to practice skills in a safe environment. Trainees can engage with lifelike simulations that mimic real-life scenarios.
While VR technology provides incredible advantages, it also presents challenges. Some users may experience discomfort or disorientation. Not every trainee adapts well to VR. It’s crucial to tailor the training programs to individual needs. This ensures optimal learning experiences for all participants.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, embracing VR can elevate training approaches. It prepares professionals for diverse medical situations. However, constant feedback and iterative improvements are essential. Addressing the limitations of VR Healthcare Training can lead to better outcomes for future practitioners.

Virtual reality (VR) is transforming healthcare training. It offers unique immersive experiences, allowing medical professionals to practice in realistic environments. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global VR in healthcare market is expected to reach $3.8 billion by 2026. This statistic highlights VR’s growing importance in training professionals across the sector.
One of the key advantages of VR is its ability to simulate complex medical scenarios. Trainees can perform surgeries or interact with virtual patients without risk. This method enhances learning retention significantly. A study from the Journal of Medical Internet Research found that learners using VR showed a 30% improvement in skills compared to traditional methods. This evidence underlines the effectiveness of VR.
**Tips:** Start with small VR modules. Focus on specific skills, like patient interaction or surgical procedures. Frequent practice in virtual settings fosters confidence. Regularly collect feedback from trainees. Understand areas that need improvement. Balancing VR with other teaching methods may yield better results. Embracing this technology could bridge gaps in healthcare education.
Virtual Reality (VR) is transforming healthcare training. With immersive experiences, it enhances learning outcomes significantly. A study published in the Journal of Medical Education reported that VR training can improve knowledge retention by up to 75%. This suggests the importance of integrating VR into training regimes.
Key components of effective VR training programs include realism, interactivity, and feedback. Realistic simulations prepare trainees for real-life situations. For instance, lifting the constraints of traditional methods allows learners to practice surgical techniques in a safe environment. According to a recent report, 85% of healthcare professionals felt more prepared after VR training sessions.
Tips: Ensure your VR scenarios mimic real-life clinical challenges. Engage learners with interactive elements. Regular feedback is crucial. It helps students identify areas needing improvement. Remember, VR training should complement, not replace, traditional education methods. Underestimating this balance may hinder overall training effectiveness.
This bar chart illustrates key effectiveness metrics of VR training programs in healthcare. Metrics include knowledge retention, skill application, engagement level, training cost, and time required, reflecting the advantages of implementing VR in healthcare education.
Integrating VR technology into healthcare education presents a transformative opportunity. Research shows that VR can enhance learning outcomes by 30%. This immersive approach engages learners more effectively than traditional methods.
To start, institutions need proper VR content tailored for medical training. Developing realistic simulations is crucial. Programs should focus on skills like surgery and patient interaction. One study revealed that 85% of participants felt VR improved their skills retention. Regular updates and feedback from educators ensure relevance and effectiveness.
Creating a supportive environment for users is essential. Training the trainers is vital to harness VR's full potential. Many educators may resist new technology due to comfort with established methods. Addressing this resistance and ensuring adequate training for instructors can foster a successful integration. Data indicates that consistent practice leads to increased competency, but achieving this takes time and patience. VR is not a perfect solution and still faces technical limitations, which require ongoing evaluation.
Virtual Reality (VR) is transforming healthcare training. Many institutions are adopting VR to enhance learning experiences. It allows for immersive simulations that replicate real-life scenarios. This approach helps trainees engage with complex medical procedures safely. For instance, a surgical VR simulation can enable a resident to practice techniques without risking patient safety.
Evaluating the effectiveness of VR training requires careful consideration. Some studies show improved retention of skills and knowledge compared to traditional methods. Trainees often report increased confidence after using VR. However, not all research yields positive results. A few participants may feel overwhelmed or anxious in high-pressure scenarios. Feedback from these individuals is crucial for development.
Moreover, accessibility remains a concern. Some institutions lack the necessary technology or resources. This can create disparities in training quality. It's essential to reflect on these challenges while embracing VR. Striking a balance between innovation and practical implementation is key. Ongoing assessment of VR tools will help refine their applications in medical education.
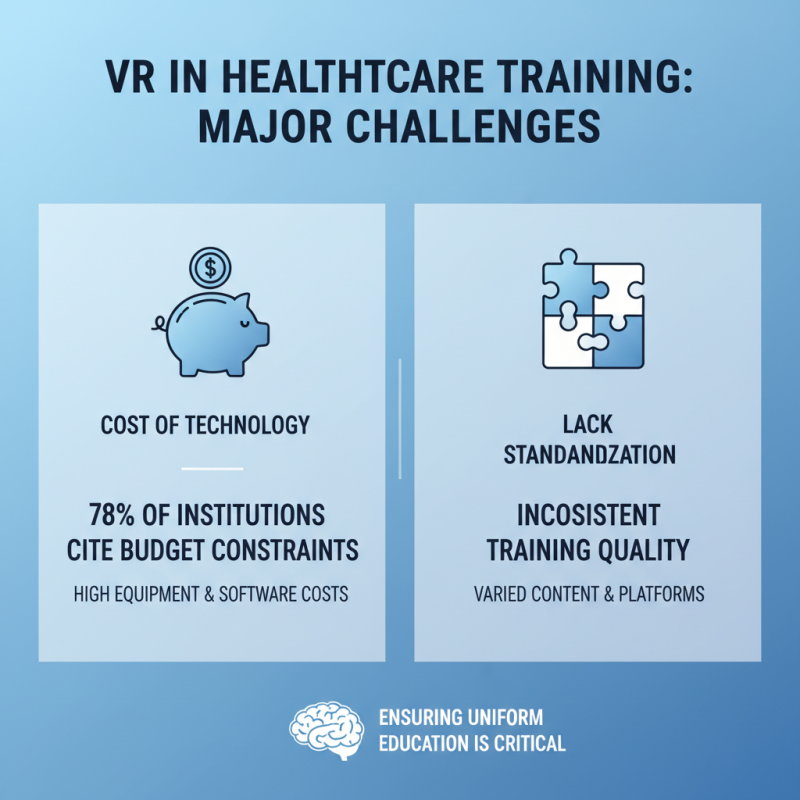
Implementing VR in healthcare training presents significant challenges. One major hurdle is the high cost of VR technology. A report from the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society noted that 78% of healthcare institutions found budget constraints limited their ability to adopt VR solutions. Moreover, a lack of standardization in VR content raises concerns about consistency in training quality. Ensuring that all personnel receive the same level of education through VR is critical.
Technical barriers also exist. Healthcare staff may lack the required technical skills to operate VR systems effectively. A study by the Journal of Medical Internet Research indicated that 58% of healthcare providers reported discomfort as a barrier to VR adoption. This underlines the need for thorough training in VR usage and integration into existing curriculums.
Tips: Consider pilot programs before full implementation. Small trials can identify potential issues early. Additionally, involve end-users in the development of VR content to ensure relevance and effectiveness. Gather feedback continuously to improve the training experience. Lastly, invest in user-friendly interfaces to alleviate technical challenges and foster engagement among healthcare professionals.