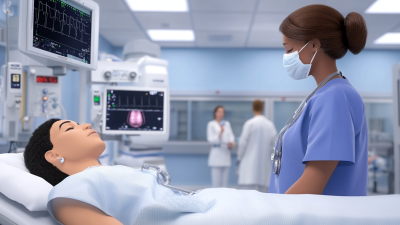
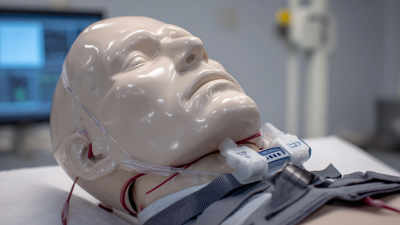
A Medical Mannequin serves as a vital tool in healthcare training. These lifelike models allow medical students and professionals to practice procedures without risk. From basic CPR techniques to advanced surgical simulations, the applications are vast.
Instructors can demonstrate various diagnostic methods on these models. Students can gain hands-on experience that traditional textbooks cannot provide. Yet, the use of Medical Mannequins can sometimes feel disconnected from real patient interactions. While they offer a safe learning environment, they cannot fully replicate human responses.
These mannequins come in various forms, some even equipped with technology to simulate vital signs. However, despite their advancements, they are not perfect. Trainees may still face challenges when moving from mannequin practice to real-world scenarios. Thus, critical reflection is essential as students transition from the classroom to clinical settings.
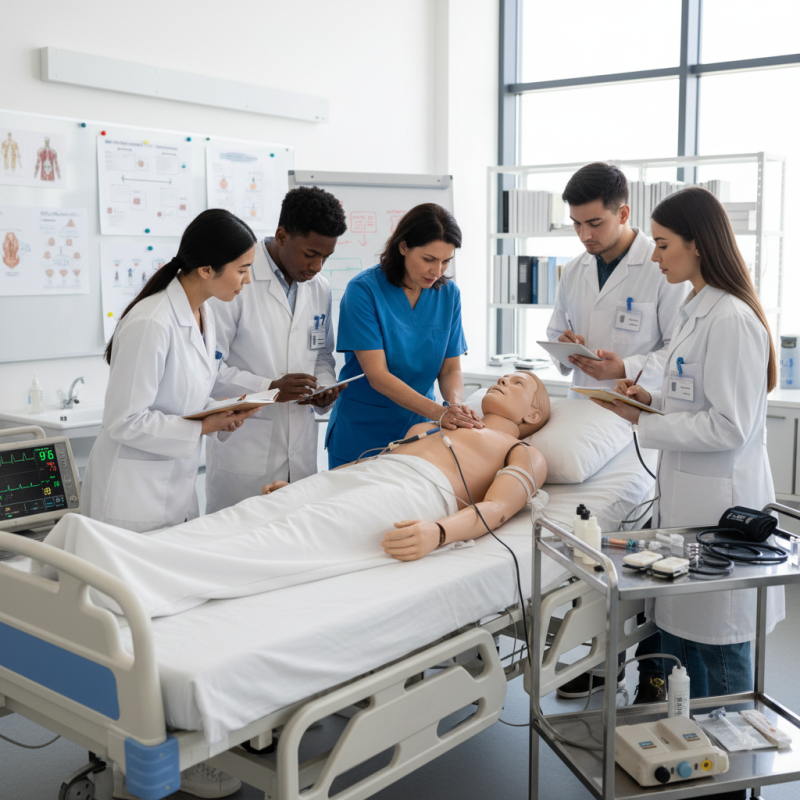
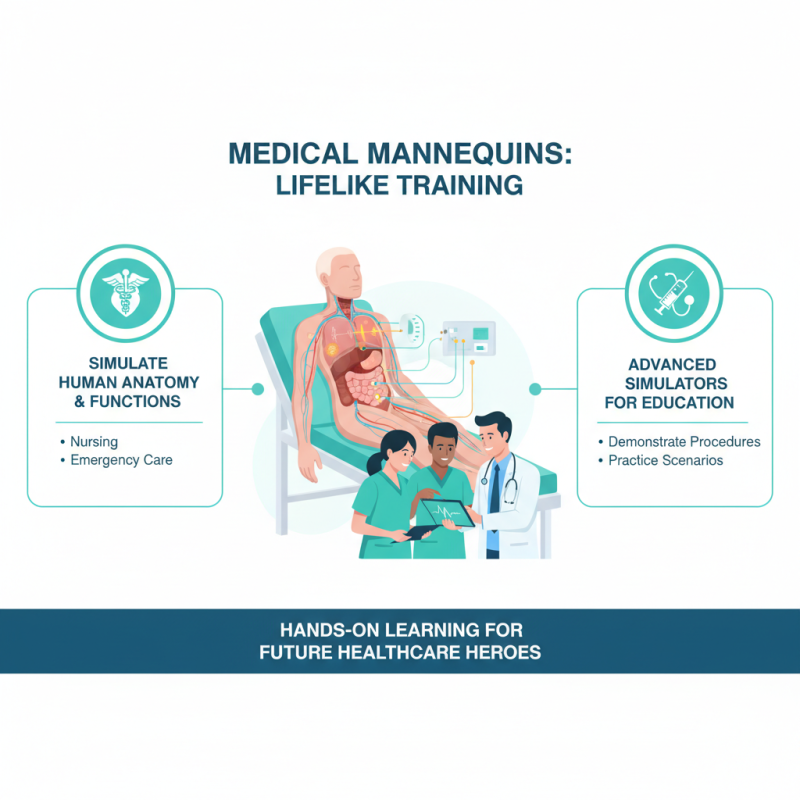
Medical mannequins are lifelike models used in healthcare training. They simulate human anatomy and functions. These tools help educate students in various fields, such as nursing, medicine, and emergency care. Instructors can demonstrate medical procedures and scenarios using these advanced simulators.
These mannequins vary in complexity. Some respond to treatments, displaying vital signs. Others allow students to practice physical exams. Flaws exist in realism and function. Sometimes, the programming may not reflect real-life scenarios. This can lead to misunderstandings or improper practice. However, they remain essential for hands-on learning.
Practicing with a medical mannequin promotes confidence. Students gain experience without putting real patients at risk. It’s a safe way to learn and make mistakes. Reflecting on these lessons helps improve skills for future situations. Mock scenarios can be challenging but teach valuable lessons.
Medical mannequins play a crucial role in training healthcare professionals. They come in various types, serving different educational purposes. Simulation-based training has become essential. Reports show that 70% of medical students benefit from hands-on experiences with these mannequins.
There are several categories of medical mannequins. Basic mannequins are often used for CPR training. They allow students to practice chest compressions and rescue breaths. Advanced mannequins mimic real human responses. These systems can simulate symptoms, pulse, and even speech. Some can be programmed to present various medical scenarios. This technology enhances learning but requires careful calibration, which can be challenging.
Specialized mannequins focus on specific medical needs. Pediatric and obstetric mannequins are designed to educate practitioners about child and maternal care. Reflections on their usage show that while they offer immersive learning, many educators feel that the realism sometimes falls short. This raises questions about training efficacy. Collecting feedback remains vital for improvement. In a fast-evolving field, ongoing updates and revisions to mannequin designs are necessary.
This chart illustrates the distribution of training hours utilized for various types of medical mannequins. Medical mannequins are essential tools in medical training, serving for patient simulation, CPR training, anatomy studies, and more. Utilizing different types of mannequins enhances the learning experience by allowing hands-on practice in a controlled environment.

Medical mannequins play a crucial role in healthcare education. These lifelike models are essential for training future healthcare professionals. A recent report from the American Association of Colleges of Nursing highlighted that over 60% of nursing schools use simulation in their curricula. This approach enhances learning outcomes and builds confidence among students.
Applications of medical mannequins are broad. They are used in skills labs, allowing students to practice procedures safely. Simulations can replicate various medical scenarios, from basic first aid to complex surgeries. According to a study published in the Journal of Nursing Education, 88% of students reported feeling better prepared for real-life clinical situations after using mannequins in their training. The ability to interact with these models fosters critical thinking and decision-making skills.
Tips: Prioritize hands-on practice. Engaging with a mannequin can reveal gaps in knowledge. Don’t be afraid to make mistakes. Use those moments to learn. Reflection on performance is vital for growth. Embrace feedback from instructors and peers. Continuous improvement is a key component of medical education.
Medical mannequins play a crucial role in the training of healthcare professionals. These life-like models allow trainees to practice various medical procedures in a safe environment. For example, students can learn how to perform CPR or insert IV lines on a mannequin. This hands-on experience is invaluable. It helps build confidence and competence.
Using medical mannequins also has specific benefits. They provide immediate feedback during practice. Instructors can observe techniques and identify areas for improvement. This direct observation can lead to better skills and understanding. Moreover, mannequins can simulate complex medical scenarios. This allows learners to experience high-pressure situations, enhancing their problem-solving abilities.
Despite their advantages, there can be limitations. Not every situation can be replicated perfectly. Mannequins lack the emotional responses of real patients. Trainees may need to adapt when interacting with actual people. This is an important reflection point for educators. Continuous improvement in training methods can help bridge these gaps. Effective training is a journey that includes embracing imperfections.
The future of medical mannequin technology is promising and full of potential. Recent studies indicate that the global medical mannequins market is expected to grow from $2 billion in 2020 to over $3.5 billion by 2026. This growth is largely driven by advancements in simulation technology and the rising need for effective training tools in healthcare.
Innovations such as high-fidelity mannequins are transforming training programs. These advanced models can mimic real human responses, including vital signs and physiological reactions. For example, a mannequin can simulate cardiac arrest, allowing students to practice CPR in a controlled environment. However, these technologies are not without their challenges. The cost of high-end mannequins can be prohibitive for many institutions, potentially widening the training gap.
There's also a growing focus on integrating virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) with medical mannequins. Research shows that immersive environments enhance learning outcomes. Yet, while the technology enhances training, it may also lead to over-reliance on simulations. This raises an important question: how can we ensure students still gain practical, hands-on experience? Balancing advanced simulations with real-world opportunities remains a critical issue in medical education.