Clinical simulation in nursing has emerged as a transformative educational approach, revolutionizing the way nursing students acquire essential skills and knowledge. This innovative instructional strategy allows learners to engage in realistic clinical scenarios in a safe and controlled environment, thereby enhancing their critical thinking, decision-making, and technical competencies. As healthcare demands evolve, the integration of clinical simulation in nursing education not only prepares future nurses for the complexities of patient care but also fosters an environment where they can learn from their mistakes without real-life consequences. This exploration seeks to examine how clinical simulation impacts both nursing education and patient outcomes, highlighting the profound implications it has for developing proficient and confident nursing professionals equipped to address the challenges of modern healthcare. By delving into the best practices and methodologies within this framework, we aim to provide insights on maximizing the effectiveness of clinical simulation in nurturing skilled nurses capable of delivering high-quality patient care.
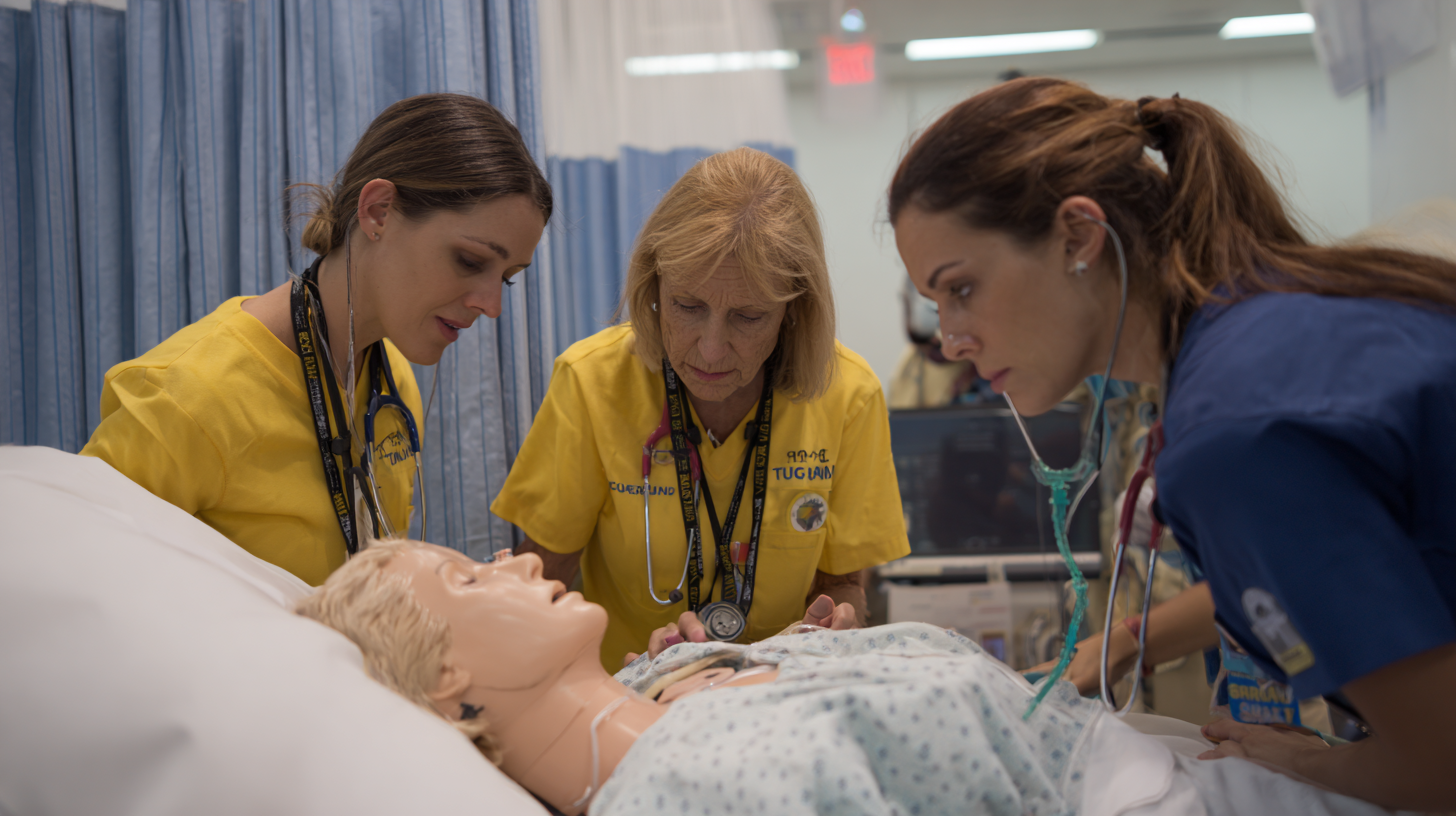

Clinical simulation has emerged as a transformative tool in nursing education, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. Defined as a pedagogical approach that utilizes realistic scenarios to mimic patient care situations, clinical simulation provides nursing students with a safe environment to hone their clinical skills. This experiential learning model allows students to practice assessments, decision-making, and critical thinking without risking patient safety, thereby enhancing their confidence and competence.
The importance of clinical simulation in nursing education cannot be overstated. It fosters an interactive learning atmosphere where students can receive immediate feedback from instructors and peers, facilitating reflective learning. By engaging in simulations, nursing students are exposed to a variety of clinical situations that they may not encounter during traditional clinical placements, allowing for a broader understanding of patient care complexities. Ultimately, clinical simulation not only enriches the educational experience for nursing students but also contributes to improved patient outcomes in real-world clinical settings, making it an essential component of modern nursing education.
Integrating clinical simulation into nursing curricula is essential for enhancing the education and preparedness of nursing students. Best practices involve creating realistic scenarios that reflect real-life clinical situations, allowing students to develop critical thinking, decision-making, and communication skills in a safe environment. By utilizing high-fidelity mannequins and virtual simulations, educators can replicate complex clinical conditions, enabling students to practice their skills without the risk of harming actual patients.
Incorporating debriefing sessions after simulation exercises is another vital strategy. These sessions encourage reflective learning, where students can discuss what went well, identify areas for improvement, and solidify their understanding of nursing concepts. Moreover, fostering interprofessional collaboration during simulations can enhance teamwork skills, as nursing students interact with peers from other health disciplines, mirroring the collaborative nature of actual healthcare settings. This integration not only prepares nursing students for clinical practice but also ultimately contributes to improved patient care outcomes by cultivating competent and confident healthcare professionals.
The effectiveness of clinical simulation in nursing education has gained significant attention as it offers an innovative approach to enhancing student learning outcomes. Through realistic scenarios, nursing students can engage in hands-on practice, developing critical thinking and decision-making skills in a safe environment. This immersive experience not only bridges the gap between theory and practice but also fosters confidence among students as they prepare to deliver quality patient care in real clinical settings.
Research indicates that students who participate in clinical simulations demonstrate improved clinical competencies compared to traditional learning methods. Assessment tools such as structured rubrics and standardized patient feedback have been employed to measure these outcomes effectively. Furthermore, simulations foster collaborative learning, encouraging students to work in teams and communicate effectively — crucial skills in the dynamic healthcare environment. As nursing educators continue to integrate simulation into curricula, the focus remains on enhancing learning, promoting retention of knowledge, and ultimately translating these skills into better patient care outcomes.

Clinical simulation has emerged as a transformative approach in nursing education, greatly enhancing patient care outcomes. Recent studies indicate that incorporating simulation into nursing curricula can lead to improved clinical skills, enhanced critical thinking, and heightened confidence among nursing graduates. A report by the National Council of State Boards of Nursing found that 70% of nursing programs now use simulation to replace traditional clinical hours, underscoring its growing significance in nursing education.
The application of clinical simulation extends beyond educational settings and directly impacts patient care. For instance, healthcare facilities are increasingly relying on high-fidelity simulations to prepare nursing staff for real-world scenarios, leading to better preparedness and reduced errors in patient treatment. A recent forum highlighted the importance of strengthening faculty development in simulation-based education, emphasizing that well-structured training leads to more proficient nurses who can provide safer patient care. Additionally, patient satisfaction scores have been reported to improve in facilities that implement simulation training for their staff, showcasing its effectiveness in bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application in clinical settings.
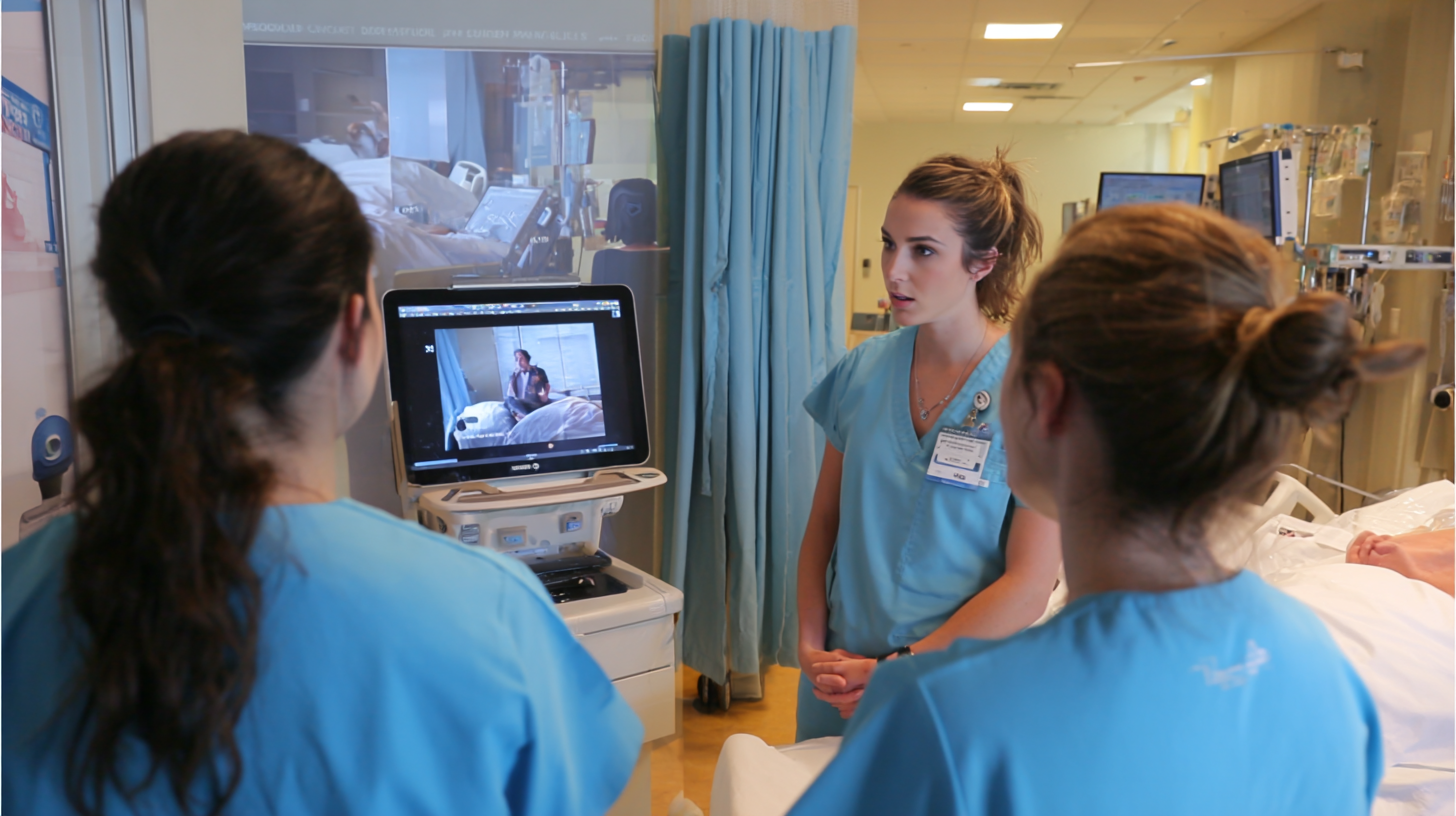

The integration of clinical simulation in nursing education is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and a focus on enhancing patient safety. According to a report by the National League for Nursing (NLN), nearly 90% of nursing programs in the United States now incorporate simulation as a fundamental teaching strategy. These simulated environments provide students with the opportunity to practice clinical skills and critical thinking in a risk-free setting, significantly improving their readiness for real-world challenges.
Future trends indicate that innovations such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are set to transform the landscape of clinical simulation. A study published in the Journal of Nursing Education highlighted that VR technology can lead to an increase in student engagement and knowledge retention by up to 60%. By immersing students in realistic scenarios, these tools not only enhance learning experiences but also contribute to better patient outcomes by ensuring that future nurses are well-prepared for the complexities of patient care.
As these technologies become more accessible and cost-effective, their widespread adoption in nursing programs is expected to further bridge the gap between education and practice, ultimately prioritizing patient safety and quality care.